
Figure 1: USB charging ports are a common requirement in office furniture today.
As a supplier of sophisticated commercial office workstations, we at Innovant are repeatedly asked about the USB charging capabilities of the many options of convenience power we provide. Some of these questions are asked by people who may as well have a PhD in USB technology. However, many other inquiries come from clients and designers who have less of an understanding of what constitutes a “good USB charging solution.”
Understanding the inner design of USB ports and cables is not needed to understand how to provide an appealing USB charging solution for office workers at their desk. All that is required is an understanding of what the various types of USB means and how their stated charging output gets utilized by the USB charged devices currently found in the office. Ideally, understanding the future of USB and how devices will work with it will allow you to make better decisions when investing in USB charging products.
For now, let’s look at the basics. There are handful of USB ports that are commonly discussed, the table below helps summarize what they mean:

USB 1.0 and 2.0 are what you first saw on computers and laptops that provided connectivity for peripheral devices like mice, cameras and printers. Not necessarily by design, they also provided 500mA of charging power to devices like phones, albeit very slow charging. USB 3.0 is clearly identified in today’s world by the blue detail on the inside of the cable and ports. While USB 3.0 does provide notably faster charging than 2.0, its main purpose is for faster data transfer rates.

Figure 2: USB 3.0 identified with blue ports.
USB charge only ports are simply designed to charge devices and not to provide any data transfer. These are the ports we see in office furniture, coffee shop tables, airport lounge kiosks etc., and their charging rates are noticeably faster than most current data USB ports. USB Fast Charge is an even faster option available in some products (like the Ag Power Module by Innovant) and they can literally charge faster than the common wall plug adapters provided with mobile devices. This is a key talking point we have with clients and designers about USB charging, and the question we ask them to think about is simply “what is the charging output of each USB port in your furniture or accessory?”. For many, a 2000mA charge is more than enough for smart phones, but a USB fast charge accessory is really appreciated for tablets and other heavier load devices for its ability to charge these devices faster, even though they may not charge a smart phone that much quicker than the common 2000mA charging ports. The list below shows the power charging draw from many common devices:
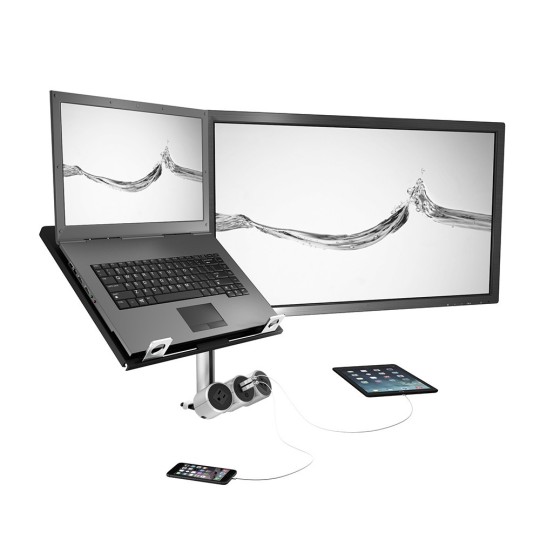
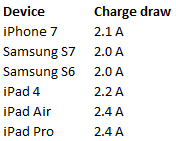

Figure 3: Innovant’s Ag Power Module with 2.5 A Fast Charging.
USB-C is a 24-pin USB connector system allowing for even greater transport of data and power. More noticeably however, is that USB-C replaces the cable connecting profile at both ends of the cable to be universal. Many people believe that USB-C could become a stable industry standard for providing data transfer and power delivery to everything from phones to laptops to lighting and even appliances. Investing in USB-C now may prepare facilities managers for such a convergence in the future. Unfortunately, at the writing of this post USB-C is simply not available as a charging accessory to office furniture. Nonetheless, we are doing our best to keep pace with an ever-changing demand for charging products, and will be sure to announce any new products that do offer this.
In a future post, we will take a look at the emergence of wireless charging devices and how they can serve dual purpose by also acting as a location service in the latest generation of unassigned or “smart” office spaces.
